Blockchain application examples
go back to acatech HORIZONS: Blockchain
Blockchain in the food supply chain

Seven years after the 2011 E. coli outbreak in Germany and the lengthy search for its cause, tracing the food supply chain is still a laborious process. Even when there is no specific threat to human health, consumers are increasingly calling for transparent and simple food traceability.
Supply chain processes involve a lot of paperwork
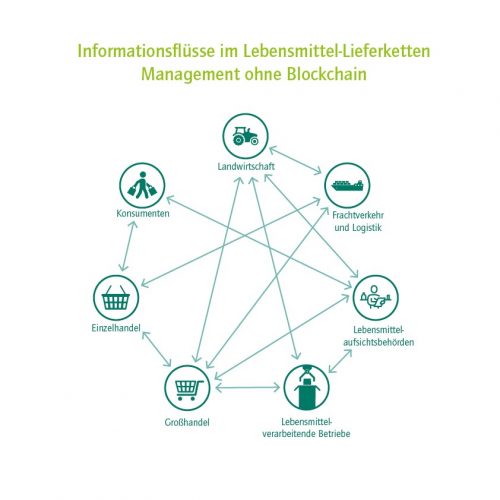
In international supply chains, it is not uncommon for information to be exchanged about 200 times by up to thirty different institutions and over a hundred people, often on paper. There is always a chance of errors creeping into this time-consuming and expensive process. Tracing the source of a piece of packaged fruit, for example, can take more than six days. Consumers find this difficult to understand.
Different read and write permissions for different participants
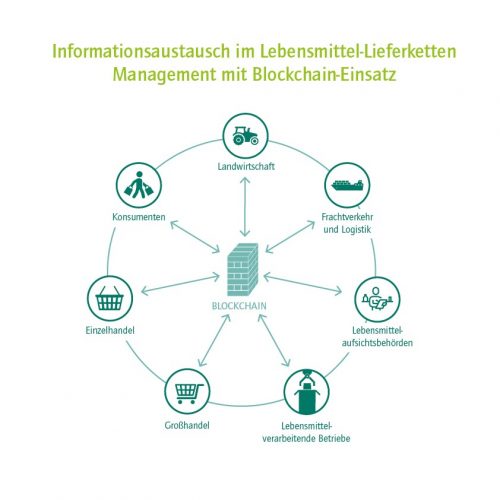
A blockchain in which participants collectively document supply chain transactions could deliver significant cost and time savings. Since blockchain ledgers can be accessed by all the participants, the trustworthiness of a central record-keeping authority would no longer be an issue. Different user groups – for example producers, carriers, customs authorities and different types of consumer – could be granted different read and write permissions depending on their needs. This would prevent competitors from gaining a completely transparent overview that they could exploit to their own advantage. For instance, end consumers would only be granted read permissions, providing transparent and verifiable traceability regarding the source of the product and the entire supply chain, including everything from harvesting to processing, logistics, customs clearance, certification, foods standards authority, wholesaler and retailer.
Opportunities for automation
Blockchain technology could also be used to automate mandatory documentation processes. For instance, a sensor installed in the container could record the temperature that the food is kept at and write the data to the blockchain, thereby documenting that there have been no interruptions of the cold chain. A smart contract would automatically generate an alarm if an interruption did occur.
go back to acatech HORIZONS: Blockchain
More application examples:
Blockchain in education
Blockchain in development cooperation
Blockchain in future energy trading
Blockchain in government and public administration
Blockchain in self-driving cars