Blockchain application examples
go back to acatech HORIZONS: Blockchain
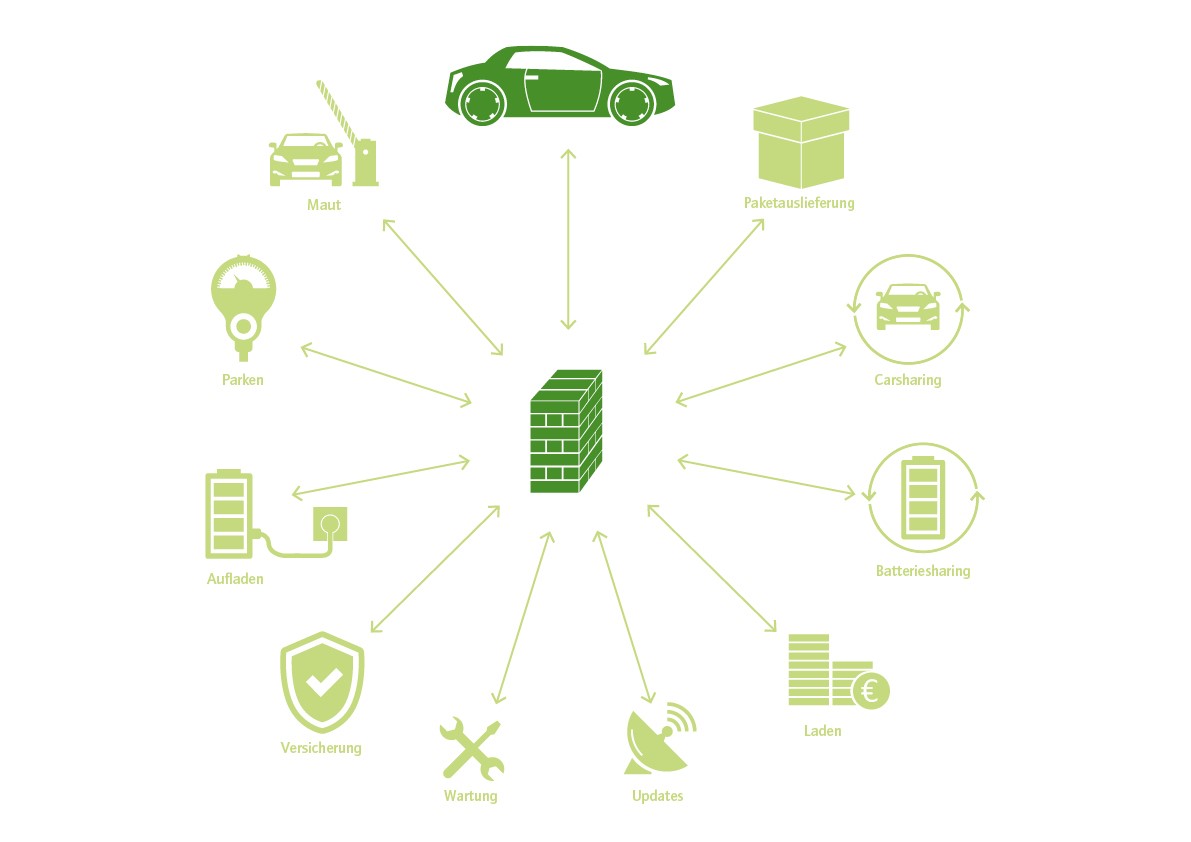
Blockchain in self-driving cars

A secure common language for smart devices and digital assistants
Because of their increasing vulnerability to cyberattacks, connected devices such as cameras and machine tools require regular security updates. Blockchains can help to ensure the security of these predominantly online updates.
The first step involves the manufacturer storing the update’s digital fingerprint on a blockchain. The device then compares the fingerprint of the downloaded update file against the entry in the blockchain. Any differences indicate that the file has been tampered with during the download, causing the device to discard the file and download the update again.
Transaction automation
If they are really to make our lives easier, devices must be coordinated and be able to exchange services with each other. Automatic coordination of devices made by the same manufacturer often already runs successfully in the background. However, problems still occur if the server responsible for managing them goes down. And complications generally arise much earlier, when people try to integrate a device made by another manufacturer.
Blockchains have the potential to develop into a decentralised, non-proprietary common language for the Internet of Things and Services. In smart contracts and tokens, they already have the basic requirements to make this possible.
One possible application would be to enable precise billing for electric vehicle charging at any charging station: all the driver would have to do would be to plug in the connector.
Self-driving and self-managing vehicles
High expectations exist with regard to the combination of self-driving and self-managing vehicles with artificial intelligence and the token economy. In the future, cars will not only operate autonomously but will also earn tokens by transporting passengers. They will use these tokens to pay for their fuel and for any repairs that they themselves deem necessary. The cars will then transfer any remaining credit to their delighted owners, who will have made some money without needing to do anything themselves.
Outlook
The experts believe that although these visions of the future can become reality, it will be some time before this happens.
Nevertheless, it is certainly worth starting to explore these types of scenarios today – work has already begun on realising some aspects. Experimenting with these ideas could lead to the discovery of new business models and forms of cooperation that would be inconceivable without blockchain.
Moreover, these long-term visions of the future highlight some of the legal, regulatory and ethical questions thrown up by new technologies such as blockchain and their interactions with artificial intelligence.
go back to acatech HORIZONS: Blockchain
More application examples:
Blockchain in education
Blockchain in development cooperation
Blockchain in future energy trading
Blockchain in the food supply chain
Blockchain in government and public administration